Along with the first digital devices rose a need to ensure the security of stored data and to differentiate access to various functions. A variety of methods for unambiguous authentication of users on which security is based are called authentication factors. These include codes, logins, passwords, certificates, hardware keys, and so on. The whole set of authentication factors can be divided into three groups:
- Factors of knowledge (something known to the user);
- Ownership factors (something that the user owns – documents or items characterized by some unique information (usually these factors boil down to “devices”, although this narrowing is not always justified));
- Biometric factors (physical characteristics of the user).

There is a huge variety of authentication factors, not all of which are equally convenient and safe. In order to raise the security level of the authentication process, multifactor authentication is used, in which several authentication factors of different types are used to verify access. The disadvantages of some factors can and should overlap by the merits of others. Despite the greater security, the more authentication stages are used, the more effort and time it takes to authorize. According to the combination of characteristics, two-factor authentication is considered the most optimal today by the combined security, convenience and applied effort characteristics.
Two-Factor Authentication
What is two-factor authentication? Two-factor authentication (2FA) is one of the most reliable types of the user authentication nowadays, used to obtain the rights to access any resource or data (from mailboxes to bank card payments). Two-step authentication is a much more reliable alternative to the traditional one-factor authentication (1FA) with the help of a login-password pair, the security of which is quite low currently. There are a huge number of methods for hacking and circumventing password authentication, from social engineering to distributed bruteforcing, based on pre-organized botnets. In addition, some users use the same password to log into all their accounts, which in turn further simplifies the access of scammers to protected information and transactions. The main advantage of two-factor authentication is the increased login security. As for the shortcomings, the main two being the increase in the time of entry into the system and the risk of losing the physical media serving to pass one of the authentication steps (mobile phone, U2F key, OTP-token). In this article, we reviewed several of the most convenient and secure second authentication factors for use in 2FA.
| Read also: Social Engineering Against 2FA: New Tricks
1. SMS Codes
SMS codes generated by special services are the most common kind of factors used in the mobile two-factor authentication. It is quite convenient (most modern users always keep their smartphones on them) and does not take much time. In addition, this check is in most cases effective, for example, to protect against automated attacks, phishing, password bruteforcing, viruses, and the like.
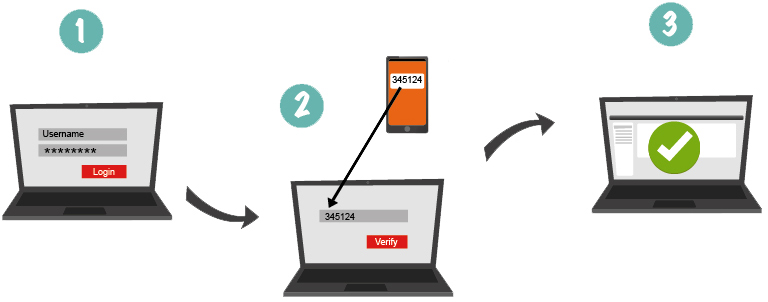
But in case someone is intent on hacking you, bypassing SMS authentication is possible. After all, usually the phone number tied to the account is not a secret (as a rule, it is the same contact number that can be found from your friends, social network or business card). Having received personal information of the owner of the number, scammers make a fake identity card and use it at the nearest office of the mobile operator. Despite the fact that in some countries the legislation requires a complete reconciliation of the ID data, SIM can be authorized for the reissuing by the most ordinary employee, not particularly bothering to verify the authenticity of the document. Thus, a new card with your number is created (in turn, the previous SIM is blocked) and the scammer gets the opportunity to pass the second stage of authentication. The second drawback is that some state authorities (for example, police) can ask the mobile operator for access to your cellular number (including SMS). This is done in real time, and even if you are eavesdropped on, you will not even know. On the other hand, SMS messages will help you find out that someone is trying to hack your account and change the password or the attached phone number in time.
Pros:
- Simplicity of the usage – the user just needs to input the code from the SMS that came to their mobile phone;
- In case an attempt to hack your account happens, you will immediately know about it, as you will receive a message with a one-time password (OTP) and can immediately change your account password.
Cons:
- Need to pay SMS sending fees. This con is especially important for the companies protecting their user. In B2B segment it’s more advantageous cost-effective to use software or hardware tokens.
- Cannot be used in case of the absence of the cellular coverage (on remote territories or abroad) or telephone itself (theft, loss, battery discharge).
- SIM swap opportunity allows attackers to steal the phone number.
- SMS messages can be intercepted with a variety of methods.
| Read also: What Hides Beneath SMS Authentication?
2. Code Generation Applications
Code generation apps are a worthy alternative to SMS codes. The most common among such applications is the Google two factor authentication solution – Google Authenticator. Such software OTP tokens generate codes independently based on a particular algorithm or random sequence. The main algorithms for generating such one-time codes are the HOTP (hash-based one-time password, RFC4226), TOTP (time-based one-time password, RFC6238) and OCRA (OATH challenge-response algorithm, RFC6287) that were developed and are supported by the OATH (Initiative for Open Authentication).

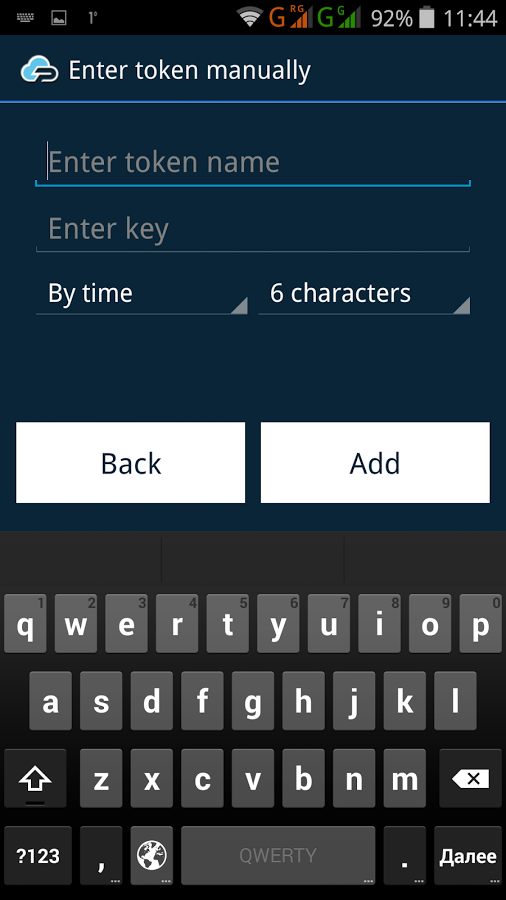
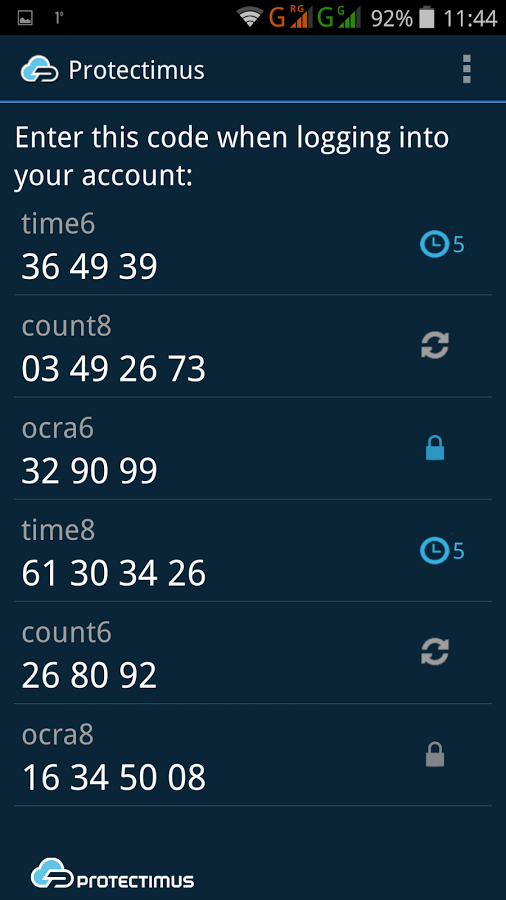
Pros:
- The main advantage of such two-factor authentication software is the possibility of using in the absence of the cellular coverage or the access to the Internet.
Cons:
- Need to use a smartphone or other similar device;
- Application can be hacked;
- Smartphone battery can discharge;
- If the smartphone is factory reset or lost, or authenticator application is deleted accidentally, the token would be lost and its recovery is a great pain.
| Read also: Hardware or Software Token – Which One to Choose?
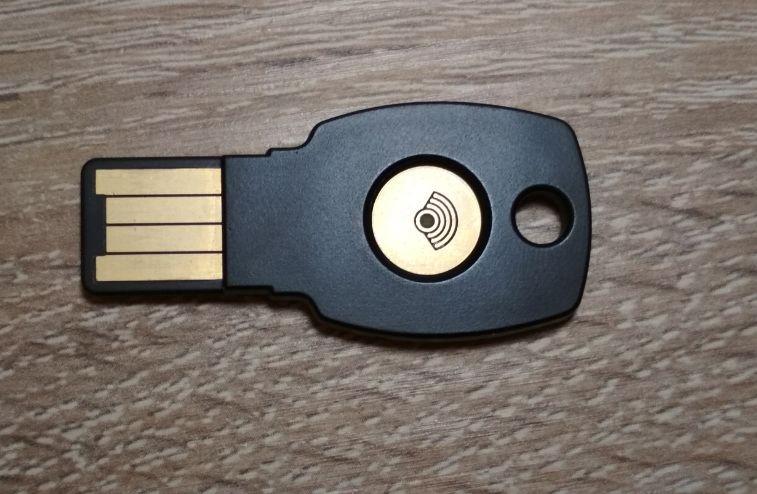
3. U2F Tokens
U2F is an open standard for universal two-factor authentication (2FA), developed by the FIDO Alliance with the participation of such world-famous corporations as Google, PayPal, Lenovo, MasterCard, Microsoft, NXP, Visa, etc. According to the creators’ idea, authentication through this protocol is carried out with a help of a hardware module, in the role of which a physical medium – USB tokens (the most common devices are YubiKey) – are used. These devices are equipped with special software and a digital key at a manufacturing stage. The USB key is simply inserted into the corresponding desktop or laptop connector. This authentication factor operates as follows:
- The user is authorized on the website/in the application using a login-password pair.
- The server checks the credentials and, if they are correct, requests the signature (generates a challenge) for the token and returns it to the user program (usually it would be a browser).
- The program transmits the challenge to the token, which, after confirmation from the user (for example, a press of a token button), returns the one-time password generated according to the certain algorithm.
- The program sends a response to the server.
- If the answer is correct, authentication takes place.
- No need to connect to a cellular network or the internet, because all the necessary data are already stored at the device.
- Ease of use – just connect the token to the USB port and press a single button when requested.
- There are Yubikey token models with two slots, which allows using them to access two websites instead of one.
Cons:
- Low prevalence, because the standard is still quite new. Currently, U2F tokens are supported by Gmail, Google Accounts, GitHub, Dropbox, LastPass and WordPress.
- U2F USB tokens, at the moment, are compatible only with the Chrome browser since version 38. This restriction is applied not by Yubikey tokens, but the U2F standard itself.
- Many companies block operations with USB ports on corporate computers.
- U2F devices are created to access 1 or 2 specific resources; an active Internet user will need to store a bundle of devices for the access to different websites.
- U2F devices are relatively costly: prices for the cheapest models start from $20.
- The token is easily forgot inserted into computer when going away from a workstation. Some people also leave them inserted all the time for the convenience, which undermines the whole concept of 2FA.
- USB connection itself leaves the opportunity of some kind of malicious code injection and trojans.
- It is desirable to buy tokens in pairs in case of loss.
| Read also: The Evolution of Two-Step Authentication
4. Contactless Hardware Tokens
A worthy alternative to the previous authentication method are contactless hardware tokens. Why do we consider this variant of tokens to be the most reliable second factor:
- They are standalone, unconnectable devices which eliminates the possibility of unauthorized external or remote access by hackers;
- They are invulnerable to the injection of malicious code;
- They allow creating a true two-factor authentication that separates something you have (a token) from something you know (a password);
- They are immune to the danger of a SIM card theft, secret key exporting, catching a virus which intercepts one-time passwords;
- Their batteries last for years, so you will never face the discharge problem during a service term;
- They do not need a cell network signal or roaming to work.

There are 2 types of contactless hardware tokens available on the market today:
- The common models with pre-installed secret keys (seeds). This is a good option if offered directly at the resource that employs the 2FA user account protection. For example, such hardware tokens are proposed by Blizzard, PayPal and AdvCash. And probably you already have similar tokens for the access to your online banking.
- But what if the website does not offer its own contactless hardware tokens? In this case, recently released programmable hardware tokens Protectimus Slim NFC would be a great help. These devices can be flashed through the NFC using the Protectimus TOTP Burner application for Android smartphones. These OTP tokens are compliant with Google Authenticator authentication server standards (32 symbols long secret key (Base32) and 6-digit OTP). Among resources that implement this standard are Facebook, Google, Dropbox, GitHub, Kickstarter, KeePass, Microsoft, TeamViewer, and many others.
Let us review both options in more detail.
| Read also: One-Time Passwords: Generation Algorithms and Overview of the Main Types of Tokens
Contactless Hardware Tokens With Pre-Installed Seeds
These OTP tokens are well-known and have been considered the most reliable one-time password generation tools for years. So why they are not so widespread as SMS confirmation and software authenticators? Mostly because shipping the devices worldwide is costly and requires notable labor resources or the cooperation with logistics company, which may be extremely inconvenient for smaller enterprises. Besides, hardware tokens are not free and many companies don’t consider them cost-effective, thus saving on the security of its users. Though some websites offer their users to purchase such tokens themselves, thus providing an opportunity to protect the account reliably.
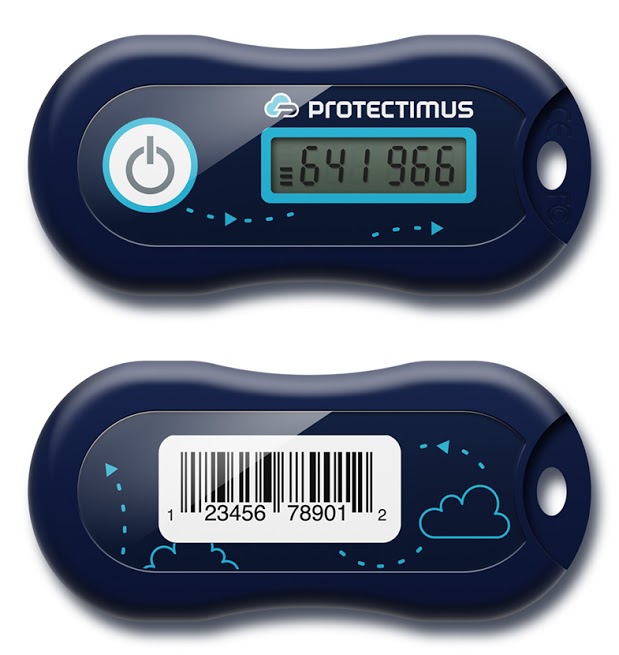

Pros:
- Contactless device, protected from any possibility of malware injection;
- One-time password is generated by the device itself, which reduces the possibility of intercept to a minimum;
- Does not require network connection of any kind;
- Built-in power source is enough for years of independent operation;
- The cheapest amongst all hardware tokens.
Cons:
- If a token is compromised, then you only need to order a new one (Protectimus Slim NFC can simply be reflashed);
- If you stop using the service, then the money was wasted, there is no possibility to use it with another service;
- If you need to protect several accounts (or accounts at different resources), you will need a separate token for each. This may lead to a bundle of varying devices which may be uncomfortable to carry around (this is also true for YubiKey, but a few slims do not take much space);
- The secret key in such tokens is pre-flashed at the factory, then passed to the supplier, then transferred to the website owner. Of course, keys are transmitted in encrypted form, but there remains a tiny possibility that at some stage an unscrupulous employee or a hacker will leak secret keys. In this respect, the Protectimus Slim NFC wins unconditionally. It is flashed by the user from their personal smartphone with a secret key that is known only to them.
| Read also: Smart Identification or How to Make 2FA More Convenient for Users
Programmable Hardware Tokens Protectimus Slim NFC
The main purpose of this token’s creation was to obtain a more universal and safe replacement to OATH-compliant code generation applications, such as Google Authenticator, Authy, Protectimus Smart, etc.

Pros:
- The main advantage of such two-factor authentication solution lies in the fact that the token can be flashed an unlimited number of times upon changing the secret key. Thus you may use it on the websites that offer only mobile authentication, change the secret key if necessary, as well as reassign it to another service if you wish.
- High level of security, since the contactless token is invulnerable to malicious code injections.
- There is no need to connect the token to any port, hence no need to disconnect it when moving away from the workstation.
- Ability to change the secret key and reflashing the token takes only three minutes.
- More versatile and less expensive, in comparison with U2F keys option (up to 40% difference in price when characteristics are comparable).
- You can order custom branding even when ordering the single token.
Cons:
- The built-in battery lasts about five years, after which the token needs to be replaced.
- Some restrictions on the size of passwords (only secret keys with a length of 16 to 32 characters in Base32 encoding are allowed), the built-in display for the challenge signature is six positioned (the standard supported by Google Authenticator). This makes such a token inapplicable to resources that employ secret keys shorter than 16 and longer than 32 characters, and eight-character one-time passwords, although such are rare.
| Read also: Why Gamers Need 2-Step Verification
5. Biometric Data
This authentication method uses biometric user data – fingerprints, facial features, eye iris or voice recognition. Undoubted advantage of this method is its unmatched convenience. You just scan a respective body part and get access. Nevertheless, currently, biometric scanners are not accurate enough to serve as reliable second factor despite being promoted as such by industry giants like Google, Samsung, and Apple. And if your biometric data is not recognized, you have to enter the recovery password which effectively defeats the whole purpose of two-factor authentication. Moreover, if your biometric factor, iris, for instance, was compromised once, it cannot serve an authentication factor anymore. Even if currently hacking the biometric scanners is hard, it is still possible and will become easier with time.
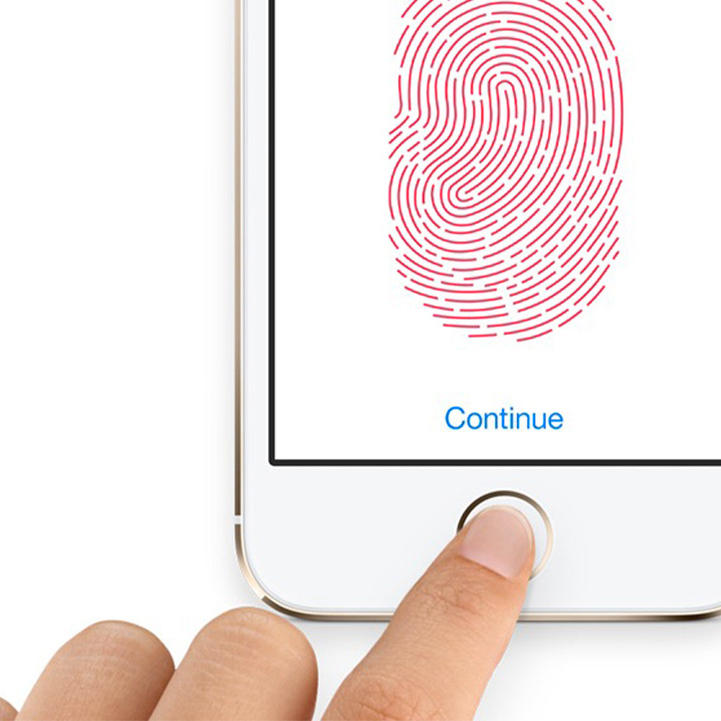

Pros:
- Convenience for the user;
- No need for physical media;
- No need to connect to any networks.
Cons:
- Extremely high cost of implementation and deployment;
- To date, the risk of inaccurate recognition is still quite high (meaning that the system can deny access due to an erroneous determination of the user’s biometric parameters). For example, the pattern of the fingers can easily be damaged by common cuts; in addition, there is a category of people – with features of temperature and body moisture – for which it is very difficult to take the print;
- If a biometric factor is compromised once, it cannot be used anymore.
| Read also: Biometric Authentication Pros and Cons
Which of the Second Factors of the Two Factors Authentication Will Suit you the Most?
The answer to this question depends on your aim. The most budgetary and easy to implement is SMS authentication or special applications for one-time passwords generation. If the need for confidentiality is very high, contactless tokens are most suitable for you, which, on the one hand, do not store any of your personal data (such as biometric information), and, on the other hand, are unique and not subject to hacking (except someone steals the device itself, which, however, can be countered). As for biometrics, its implementation is reliable only in the case when some reserve method of identification is envisaged, and it requires quite significant financial investments.
One thing should be noted firmly though – 2FA solves the problem that arises when one of the authentication factors is compromised. However, if both factors are on the same device, then there is really no two-factor authentication. To ensure an appropriate level of security, both factors must be from different groups or implemented from different devices.
Read More:
- Will Google’s Authentication without Passwords Be Safe?
- Two-Factor Authentication with Background Noise: Is It Safe or Not
- 10 Steps to Eliminate Digital Security Risks in Fintech Project
- Top 7 Tips How to Protect Yourself from Phishing Scams
- Credit Card Fraud – Most Common Ways
- 10 Basic BYOD Security Rules
- Ransomware – to Pay or Not to Pay
- Which messaging apps are trustworthy?
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.



2018-01-11
Code Generation Applications:
You can backup some tokens, text tokensto a secure notepad (AES/Blowfish2 via vim/Steganos etc) or password app (Keepass), QR image tokens: screenshot to Veracrypt/EncFS container. Then you can re-use again.
2018-10-19
I’ve enjoyed reading this, well done.
As mentioned SMS, Email and Voice Call can be easy intercepted. Software Token and Push Notifications are indeed easy to use but a Smartphone is not at all a Secure Device.
Therefore going for a Hardware Token is actually a must. However, losing Smartphone and Hardware Token happens.
So never forget to have an Emergency OTP like printed OTP List, QR Codes or a Second Hardware Token.
Keep up the good work, best regards.
2019-04-01
Here’s a topic idea for you: what 2-factor authentication can be used by the ~22% of the population who do not have smartphones? What about the ones who only use 3g flip phones? Or the ones who don’t have a cell phone at all?
Are we going to simply lock people off the internet entirely if they don’t use smart phones in the future?
Already, many sites are pushing hard to use 2-factor authentication. Some insist on a cellphone number so if you don’t have one you have to use someone else’s who doesn’t want to ever use that site.
You could ask Skype whether they are going to let people use it for 2-factor. We could send texts, but not receive them. But recently, I believe I’ve heard that we may be able to receive them now. Maybe we could use Skype for authentication?
2019-04-03
Hi Gail, thank you for the comment. You raise the issues really worth thinking about.
I’d like to mention that we already offer some authentication methods suitable for people who don’t use smartphones.
First of all, hardware tokens. Many organisations already give out hardware tokens to their customers or employees, who don’t have or don’t want to use their phones for 2-factor authentication. Most commonly these organisations are banks and large corporations who protect their employees’ data. But the tendency is quite promising, for example, you can already order hardware tokens directly from your Google or Blizzard account. Also, there are programmable tokens Protectimus Slim NFC that can be added almost to any system. You need a smartphone to program Protectimus Slim NFC, but still, you can program as many tokens as you wish with only one phone and it’s totally safe.
And secondly, there is two-factor authentication via chatbots launched by Protectimus last year. One-time passwords are delivered via chatbots in Facebook Messenger, Viber, and Telegram so far, but we are working on adding more messengers, and maybe someday it’ll become possible to add Skype as well. You can read more about this technology here: https://www.protectimus.com/protectimus-bot
2021-01-31
Very Nice JOB!