In the age of being dependent on contemporary technologies, the cybersecurity issues are as vital to pay attention to as never before. We leave a huge trace of our personal identity online. Not to mention an enormous digital trail we leave in social networks when posting photos with geolocation, reposting all news and thoughts we consider important, commenting on everything that we have an opinion about. We also use online banking almost for all our payments, as well as we use e-governance services to avoid facing bureaucracy in person, etc. Remember, every byte of such sensitive data can be stolen and used against you. You can lose all your money and even more than that if you become a victim of a hacker attack.
And one of the most dangerous and inconspicuous hacking techniques is man in the middle attack. If it happens when you transmit sensitive data to your bank or, for example, tax office, you won’t even understand that something wrong is going on, while the attacker will be stealing your login credentials and any other info he/she needs to hack you.
In this article, we’ll explain:
- what is man in the middle attack
- how MITM Attacks are performed
- how to protect your company from MITM attack
- how to protect yourself as an average user from man in the middle attacks
So, let’s begin!
What Is Man In The Middle Attack?
Before we start digging into how to stop man in the middle attack, we should be on the same page regarding what it is.
A man in the middle attack is the digital equivalent of eavesdropping. It may occur when a device transmits data to a server or website. For instance, it may be a user’s smartphone that sends the location to the server of an app installed on it or a computer sending login credentials to the bank server. The attacker can intercept the data that is being exchanged. If the connection is not secure, the attacker won’t even have to decrypt the data.
After the data gets captured, the original data is usually sent to the destination server, though in some cases the attacker can modify the information, it depends on the purpose he/she has.
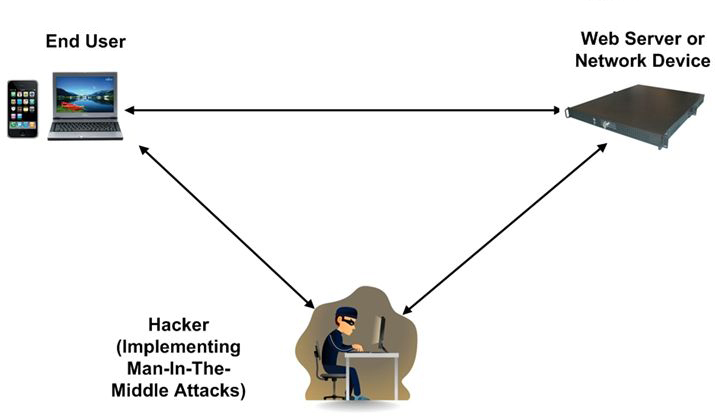
Man In The Middle Attack Explained
So, now let’s explain man in the middle attack in details. You could easily find yourself under a man in the middle attack before you even had your first computer. The thing is that there can be a man in the middle of any channel used for data exchange. For instance, unbeknownst to you, the mailman could take all the letters that you wrote, open the envelopes, read them, seal them in a way that it is impossible to see that someone opened the letter, and send them to the addressee. If you think “oh, I wouldn’t mind anyone knowing what I write in my letters”, think twice. What if you sent some legal papers? Or business plans?
If we return to our present Internet age, think again: what data do you send to servers? It could be anything from exchanging funny memes to approving transactions via online banking systems.
In the online world, a man in the middle cyber attack works in the same way. For instance, let’s imagine you connect to a Wi-Fi network that does not require a password in a public place. Of course, you don’t know that this network may be created by an attacker waiting for you to transmit some sensitive information. In this scenario, if you try to browse a well-protected website using the man in the middle Wi-Fi, you would probably get a message saying that the connection is not secure.
But if there is no such message or you don’t pay attention and decide to proceed anyway, you will see the page you were expecting to see. Everything will seem to be as usual. However, in fact, the attacker could have created a fake server that would intercept the page sent to you by the website server and modify it a bit to collect the data you enter on the page. The only difference is that such a server would not possess the necessary security certificate. This is why to prevent a man in the middle attack HTTPS is used for online banking, the login pages, emails, etc.
| Read also: Social Engineering: What It Is and Why It Works
How MITM Attacks Are Performed – 8 Key Techniques
In order to be able to avoid man in the middle attack, we need to know our enemy. So, let’s take a look at 8 key techniques that can be used to perform a man the middle attack. This will help you to protect your business and customers better.
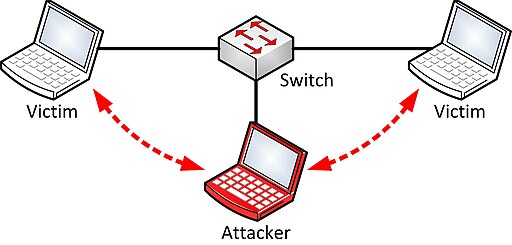
1. ARP Poisoning
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is used to resolve IP addresses to physical MAC (media access control) addresses in a local network. When a host needs to talk to a host with a given IP address, it references the ARP cache to resolve the IP address to a MAC address.
If the address is not known, a request is made asking for the MAC address of the device with the IP address. At this stage, the attacker intercepts the ARP query and sends a forged packet to the source computer. The forged packet associates the IP address from the ARP query with the MAC address that belongs to the attacker’s machine. The same thing is done to the target machine to fool it into thinking that the attacker’s machine is the sender.
Thus, the attacker can see the whole data exchange process, record the data that is being transferred, and deliver it to the target network component without both parties even noticing that there is data theft going on.
2. ICMP MITM
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a supporting protocol in the Internet protocol suite. It is used by network devices, including routers, to send error messages and operational information indicating, for example, that a requested service is not available or that a host or router could not be reached.
In case of ICMP MITM attack, first of all, the attacker looks for the network hosts that are down. When these hosts are pinged by other machines in the network, the attacker responds by sending a successful ping message. So, the machine starts exchanging data with the attacker’s machine thinking that it is the host they were looking for.
3. DNS MITM
The attacker identifies all the DNS (Domain Name System) servers that are a part of the targeted network. It can be done by searching for DNS queries that are made on port 53. After this, the attacker executes the ARP poisoning method described above to fool the source machine into sending the DNS queries to the attacker’s machine. If this attack is done, the scale of the damage that can be done to the security of the whole system has no limits. For instance, the hacker can use this attack to create a phishing website and direct all the queries to it, thus stealing any data being exchanged.
4. DHCP MITM
This type of attacks is quite similar to the previous one, except in this case the attacker intercepts DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) queries and responses. It allows the attacker to see a complete map of the network including all the MAC and IP addresses, DNS servers, etc. Such information is usually collected for planning more advanced attacks on the network. For instance, the attacker may assign the same IP address to all the hosts on the network, thus paralyzing the whole network.
5. Cookie Hijacking
A cookie is a small set of data that is created by a certain website and sent to the user’s computer to be stored in the user’s web browser while the user is browsing. Cookies are used primarily in order to make the user experience on this website better and more pleasant: cookies record the data about the user’s settings, preferences, and activity on the website.
But the cookies can be stolen by the MITM attacker from the browser in order to be seen as the user by the web server and, for instance, access the user’s account without going through user authentication. The cookies can be intercepted in three ways:
- by stealing them from the computer that they are stored on;
- by hijacking the browser session;
- by intercepting the data being transferred over the wire.
| Read also: General Data Protection Regulation Summary
6. Man In The Browser
This type of attack is carried out by placing malware, either a Trojan virus or a malicious script, on the user’s device and exploiting some yet unfixed vulnerabilities of the browser itself or the operating system on which the browser is running. This allows the attacker to have access to the whole web session and control what data is sent to the website server. Such sort of man in the middle attack is especially dangerous because such common security features as SSL encryption are useless for preventing it. What can the attacker do when performing such an attack? Well, let’s imagine that the user is shopping online and enters the delivery address. The attacker can hack into transmitted data and send his or her own delivery address to the web server without the user even noticing it, etc.
7. SSL MITM
SSL protocol works on the public key cryptography concepts. In a healthy situation, when a client such as a browser tries to connect to the secure server, the server provides its certificate to the browser. The browser then checks it against its own list of valid and trusted certificates and verifies the information contained in it. Once the certificate is accepted, the server and browser both negotiate on a common level of encryption to be used, create a key and transfer data in the agreed encryption form. If the certificate is expired or non-trusted, the browser flashes a warning to alert the user who is using it.
In order to perform the SSL MITM attack, the attacker intercepts the traffic exchanged between the browser and the server, inserts his machine into the network, and fools the server into negotiating the shared secret (in order to determine encryption method and the keys) with his or her machine. The data that ends up transferred to the browser is unencrypted and can be collected by the attacker.
Another way to execute such man in the middle attack in network security is to install an edited certificate directly to the user’s computer that allows the attacker to establish a secure connection with both the browser and the server. In this case, it is impossible for a regular user to see that his or her data gets stolen as the connection is displayed as HTTPS.
8. Wireless MITM
Attacks that exploit the wireless network weaknesses are even easier to execute than the ones that require hacking into the wired network. If the security measures are not sophisticated enough, they will not even detect man in the middle attack. Thus, there is a number of ways the attacker can steal data over the Wi-Fi connection:
- using a dummy access point with the same SSID and a stronger signal while disrupting the users’ traffic to the legitimate router;
- gaining access to the legitimate router by hacking into it using the brute force method and making a bridge to the attacker’s router;
- faking the legitimate router’s MAC address.
Where Man In The Middle Attack Can Reach You
Now that we know how attackers may steal your data, let’s review the most common situations where you can fall victim to a MITM attack.
Wi-Fi Networks
As we have mentioned above, stealing data over a wireless network is easier than from a traditional wired one. So, first of all, you should be extremely careful when you connect to open Wi-Fi networks in such public places as airports, cafes, etc. However, even a secure wireless network can be hacked into by the brute force. Besides, the attacker can hijack a secure wireless network by redirecting the traffic to his or her own Wi-Fi node or faking the MAC address of your router. So, any wireless network can be under a MITM attack.
Browsers
MITM attacks can reach you within your own browser as well. The most frequent aim of installing malware on the computer is to modify the details of financial transactions that are made via the browser. The danger of this attack is that the user doesn’t suspect that the details of the transaction (e.g. the amount of the payment or its destination) is altered. Besides, this malware can go unnoticed by the antivirus, and it can also bypass encryption.
Smartphones
Your smartphone can also be under attack. The attacks targeted at smartphones are usually carried out in order to intercept the content of SMS, including the ones that contain the codes for user identification on various websites. To do this, the attacker infects the phone with malware that will capture all the SMS traffic and scan it for authentication codes.
Apps
The attacker can exploit the weaknesses in the app’s security to insert a fake certificate into the app. Thus, the attacker can intercept all the data that is being exchanged between the app and the server, as well as impersonate the user within the app. If your mobile banking app gets attacked, your finances may end up in the hands of the attacker.
Cloud Services
There is a number of ways the hackers can get to you and your files on Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, Dropbox, etc. The thing is that most of the cloud-based storage services provide you with the opportunity not to log in every time when your account synchronizes shared files uploaded by someone else. In order to make sure that you are you in this situation, the server provides all engaged users the so-called “synchronization token” for user authentication purposes. However, it can be stolen or intercepted by the attacker in order to upload malware or steal files that are stored in the cloud.
Internet-of-Things Networks
This is a relatively new thing in the world of MITM attacks. The data from any component of the IoT network can get intercepted by the attacker, including the data from our cars, TVs, refrigerators, and any other electronic appliances that are a part of the network. Unfortunately, these objects are usually designed with the assumption that they won’t be a target for hackers. So, they do not tend to have an in-built security system that would be a good man in the middle attack prevention tool.
| Read also: 10 Steps to Eliminate Digital Security Risks in Fintech Project
Man in the Middle Attack Prevention
There is a wide range of techniques and exploits that are at attackers’ disposal. However, there is no reason to panic – find out how you can prevent man in the middle attacks to protect yourself, as well as your company’s network and website, from the man in the middle attack tools.
How To Protect Your Company Network And Website From MITM Attacks
Let’s start with enhancing corporate security. There are 7 efficient ways to protect your business from MITM attacks:
- Implement Authentication Certificates
Man in the middle attacks can be prevented by using certificates that authenticate the machines that operate within the network as legitimate ones. Under the authentication system based on certificates, any machine that attempts to operate within the network has to provide a particular certificate to gain access to it. This type of MITM attack prevention doesn’t require all your employees to become security experts – installing the certificates and updating can be automated and doesn’t require any additional hardware.
- Introduce WEP/WPA Encryption
This mechanism of man in the middle protection guarantees that all the data transmitted over a wireless network is encrypted. Thus, unwanted users won’t join your network just being nearby and even if the attacker manages to intercept the data exchanged over the wireless network, it will be unreadable. Besides, strong encryption, especially when reinforced with a strong password of at least 12 characters long, will ensure that only the users who have necessary credentials will join the network.
- Monitor The Web Traffic In Real Time
It is unwise to save on man in the middle attack countermeasures. So, invest in an up-to-date man in the middle attack detection solution. Such solution is supposed to track all the web traffic created by the system and users’ machines at both port and protocol layers, and it can flag abnormal and/or malicious activities as potential security threats and block them if necessary, all in real time.
- Invest In Confirmation Software – Data Signing
Remember that the attacker can modify the data the user sends to the server? For instance, the user makes a transaction to another bank account address that is displayed on the screen. At this moment the attacker can modify the address that is actually sent to the bank server in order to get money to his own bank account. To avoid this, invest in advanced software that makes sure that the user confirmed what he or she sent. At the same time, make sure that the attacker could not use the user’s signature to verify a fake transaction. For instance, Protectimus designed the Confirm What You See (CWYS) solution exactly for such cases. CWYS function allows generating one-time passwords on the basis of transaction data – the name and bank account address of the recipient, the amount of transaction, currency, time, etc. Even if the hacker intercepts such OTP password, it will be useless to him, because it won’t sign any other transaction except the real one created by the user. You can try a demo version here.
- Educate Your Employees
All the investments you make in the advanced security solutions will not help you if your employees aren’t well-aware about the potential threats and don’t know how to detect man in the middle attacks. So, introducing a comprehensive man in the middle attack tutorial can eliminate the possibility of data leak.
- Opt For HTTPS, Get Rid Of HTTP
As for the website security, there are also several options for the efficient man in the middle attack mitigation. First of all, make sure your website runs on HTTPS instead of HTTP and check every link and page element, especially login forms. Disable outdated security protocols and ensure only TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2 are enabled. Also, use HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) security policy mechanism for MITM protection – it will not allow hackers to redirect users to an HTTP version of your website.
- Create VPNs
VPN can be used to create a subnet within the frame of a local network that is secure for exchanging sensitive data. Key-based encryption will ensure that all the traffic is encrypted, and only the authorized parties are able to see the decrypted data. So, VPN man in the middle attacks are pointless and difficult to perform. For additional security protect your VPN with two-factor authnetication.
| Read also: 10 Basic BYOD Security Rules
How To Protect Yourself From MITM Attacks
It is not only corporate security you should worry about. You personally can be under a MITM attack and lose your hard-earned financial resources or get blackmailed as the result. In order to avoid this scenario, follow the personal security tips listed below.
- Browse HTTPS Sites. Make sure that you are browsing the HTTPS version of the website. You can do it by checking the URL bar. You can also install a plugin like HTTPS Everywhere to your browser – such plugin will find out if there is the HTTPS website version available and will download it under any circumstances.
- Be Cautious With Public Wi-Fi Networks. Avoid connecting to open Wi-Fi networks, especially if they are not protected by a password, at all costs. If you have no choice at the moment, do not use it for logging in and especially for making financial transactions.
- Invest In A Good Antivirus. Antiviruses are designed to detect the malware that attackers may attempt to install on your device. So, keep your antivirus up-to-date, and install the updates for your operating system and the browser regularly as well.
- Pay Attention To Certificate Warnings. If you see a message saying this website has a certificate issue, don’t even think to proceed to it anyway. It is an obvious suggestion; however, you’d be surprised how many people click through this warning.
| Read also: The Most Common Ways of Credit Card Fraud
Conclusions
Man in the middle attacks are the digital equivalent of the good old eavesdropping. It can be carried out in a number of ways (ARP Poisoning, ICMP MITM, DNS MITM, DHCP MITM, Cookie Hijacking, Man In The Browser, SSL MITM, Wireless MITM, etc.). It can reach you within the WiFi networks that you use, your smartphones, browsers, mobile apps, cloud services of your choice, IoT networks.
So, what procedure can prevent man in the middle attacks? The takeaway for corporate security is:
- implement the authentication system based on certificates;
- introduce WEP/WAP encryption;
- monitor the web traffic in real time;
- invest in confirmation software;
- educate your employees;
- opt for HTTPS, get rid of HTTP;
- create VPNs.
As for your personal security, you can avoid MITM attacks by:
- browsing HTTPS sites;
- being cautious with open WiFi networks in public places;
- investing in a good antivirus;
- paying attention to certificate warnings.
Take care of your cyber security and remember: the attackers are always working on new ways to perform MITM attacks.
Read more:
- Strong Customer Authentication According To PSD2: Summary & Checklist
- Ransomware – to Pay or Not to Pay
- Malvertising: Can It Be Stopped?
- What is Online Skimming and How to Avoid It
- The Pros and Cons of Different Two-Factor Authentication Types and Methods
- How to Backup Google Authenticator or Transfer It to a New Phone
- 10 Most Popular Two-Factor Authentication Apps Compared
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.


2018-05-30
Nice, descriptive, well managed and explained information.
Thanks for the post.
Keep posting !!!
2018-05-31
Dear Atul, thank you very much for encouraging words! It’s a great pleasure to hear that you like the article.
2018-09-10
Sometimes it happens when we comment on so many websites. There are many Types of Viruses in Computer Like Boot Sector Virus, Direct Action Virus, Resident Virus, Multipartite Virus, Polymorphic Virus, Overwrite Virus, Spacefiller Virus and all.
2019-07-31
This is a great article! Thank you so much! I’m new to cryptography, and MiTM confused me for quite some time. For anyone who is looking for another basic/intro article to MiTM, I found a wonderful piece: doubleoctopus.com/blog/the-ultimate-guide-to-man-in-the-middle-mitm-attacks-and-how-to-prevent-them/ I hope others find this helpful!
2019-08-01
The technique of MITM prevention and detection is really great to see. This is really a unique technique you are explaining and it’s really looking great. I also apply this technique. I must say the well-explained process.