Currently, there is a large number of similar terminology used in the field of ensuring international information security, even sometimes without getting a generally recognized definition. The most controversial debates on global markets in the field of international information security (IIS) are more focused on the interpretation of the terms «cybersecurity» and «information security» and related semantic nuances.
Telling the difference between terms like «cybersecurity» and «information security» is quite relevant, because nowadays a lot of banking regulatory agencies request banks to implement own cybersecurity systems and IIS security policies. Therefore, it is necessary to know what these definitions are, which side the threat can come from, and how it can be prevented.
So, what is the difference between these two terms?
Information security (sometimes shortened to InfoSec) is usually understood as the protection of information of the whole company from deliberate or accidental actions leading to damage to its owners or users. First of all, information security is aimed at risk prevention. More often, financial documents, logins and passwords for entering the network of different organizations are taken away from the companies. As it happened in July, 2017, when at the Equifax credit history bureau in the US largest personal data loss occurred. The attacker got personal information of more than 143 million consumers and 209,000 credit card numbers. All in all, on September 8, 2017, the shares of the bureau fell by 13%.
While creating the program for information security the special attention should be drawn to the correct management structure you apply. InfoSec experts seek to exploit the CIA (which is the abbreviation for its three components) as a manual for developing policies and procedures for an efficient information security program. The triad components are as follows:
- Confidentiality: The primary objective is access limitation to information. As a case study an account routing number while banking online may be used. The encryption of data is an overall method of providing confidentiality. IDs and passwords compose a model procedure; two-factor authentication is becoming the standard. Biometric authentication, hardware and software security tokens are also popular options.
- Integrity: It endorses the data coherence, exactness, and reliability throughout the life cycle. Data should not vary in transit, and all actions are aimed at guaranteeing that data won’t be changed by unregistered people.
- Availability: Authorized users should have easy access to necessary information in case of need, and all software and hardware should be provided adequately and updated regularly.
| Read also: General Data Protection Regulation Summary
The CIA triad constitutes the rule sample for securing your organization. It’s three constituent elements present a strong set of safety controls in order to store and save your data.
Actual kinds of information security threats:
- First of all and the most popular reason is employee carelessness and negligence. In 2010, the iPhone 4 prototype was left in the pub by one of the Apple employees, Gray Powell. There were still several months before the official presentation of the gadget, but one student found it and sold it for $5,000 to Gizmodo journalists, who in turn made an exclusive review of the novelty.
- Using pirated software. In accordance with the Microsoft research, 7% of the studied unlicensed programs contained special software for stealing passwords and personal data.
- DDoS-attacks (Distributed-Denial-of-Service). Usually, these attacks are used in the matter of competition, blackmailing companies or to distract the attention of system administrators from certain unlawful actions, such as the abduction of funds from accounts. As experts say, theft is the key motive of DDoS attacks.
- Viruses. Recently, the so-called cryptographic viruses have become particularly active. In the spring and summer of this year, millions of users were affected by attacks of the viruses named NotPetya, Misha, WannaCry. According to Intel, the virus WannaCry infected 530 thousand computers, and the total damage to companies amounted to more than $1 billion.
Among the means of information protection next methods can be identified: Physical Information Security (HID-cards), Anti-DDos, Data Backup, Disaster Recovery Plan, Encryption of data in the transmission of information in electronic format (end-to-end protection).
| Read also: 10 Basic BYOD Security Rules
So what is the Cybersecurity then?
Cybersecurity deals with saving assailable soft within Information and Communications Technology (shortened ICT). The place of data storing and technologies which may be applied should be taken into account. Part of ICT security is hard and software. Cyber security is all about protecting data in its electronic form.
The Venn diagram depicted below will help us to understand the differences between InfoSec and Cybersecurity.
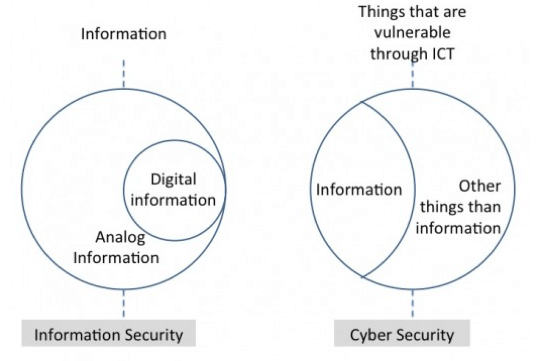
The diagram above depicts the cybersecurity spheres (assailable things within Information and Communications Technology). In Cybersecurity round there is an information area itself, and other things area (for example, electronic appliances, and so on). The Information security round in its turn consists of an analog information, and it’s part digital information.
An interesting fact is that only 15% of companies from the oil and gas industry have a formalized program for responding to cybersecurity. This is evidenced by the results of a study conducted by experts of the British audit and consulting company Ernst & Young.
| Read also: 10 Steps to Eliminate Digital Security Risks in Fintech Project
When a company becomes a target of cyber-threat attackers, notice that not only a business but also employees come under research. They count on the fact that the workers of the IT sphere are not ready for cyber attacks, so they manage to use people who do not even understand this. During the social engineering process, threat attackers manipulate people into proving the access to vulnerable information. This kind of attacks can be divided into several categories:
- Phishing scams: phishing takes place while mailing or in chats, where the threat attacker pretends to be a real organization to get some personal data.
- Explaining away: The goal is to make the attacked person believe in the truthfulness of the attacker position and give information.
- Lure: The idea is in intentionally lost infected device (USB or CD) in a place, where a person may easily find it. The infected device comes on the computer and installs the malware by chance, which gives an access into the person’s system.
- Compensation: An attacker asks an access to the information for a certain compensation, like gifts, money or services.
Thus, in order to ensure the preservation and protection of intellectual property, confidential customer information and other information important for business, it is necessary to have a comprehensive security strategy that is closely aligned with the goals and objectives of the business. The problem is that the number of cyber attacks has increased, and the employees are not always aware of the possible danger. For all this, it is necessary to distinguish and understand spheres like Cybersecurity and InfoSec, and also know how to prevent information leak.
Read more:
- Identification, Authentication, and Authorization – What’s the Difference
- Phishing, Vishing, Smishing, Pharming – What Is the Difference
- The Most Common Ways of Credit Card Fraud
- 10 Most Popular Two-Factor Authentication Apps Compared
- Strong Customer Authentication According To PSD2: Summary & Checklist
- How to Backup Google Authenticator or Transfer It to a New Phone
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.

Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from Protectimus blog.
You have successfully subscribed!